FLIES
Often underestimated in livestock production and agricultural settings, flies such as horn flies, face flies, stable flies, and house flies can pose significant threats to your animals, employees, and overall productivity. These pests can feed on livestock, spread diseases, and contribute to various health issues for both livestock and humans. Starbar® has expanded its portfolio of insect control products to combat horn flies, stable flies, face flies and house flies to protect your livestock and operation from the detrimental effects of these fly infestations. Continue reading to explore more about these common agricultural pests and discover the Starbar® products designed for effective fly protection in and around your facility.
TYPES OF FLIES

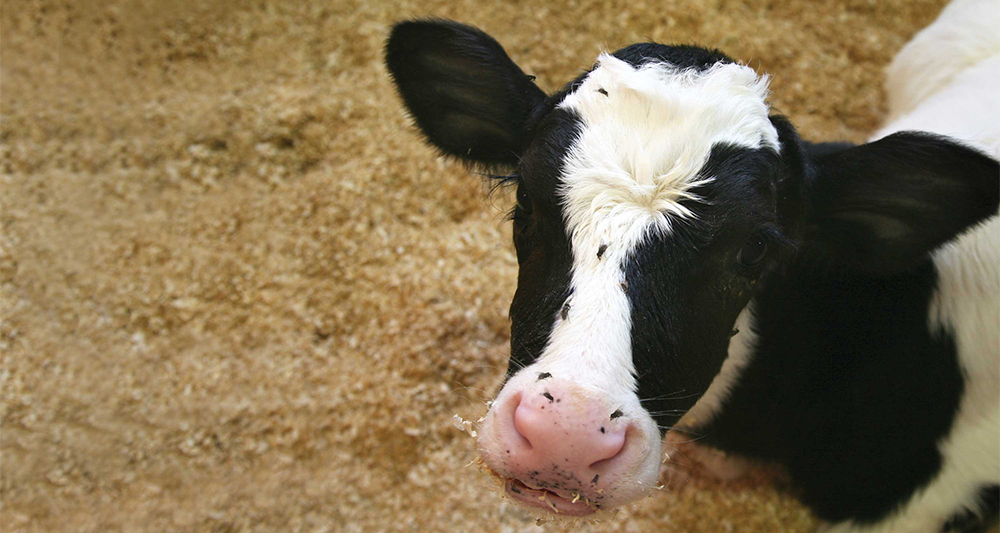
Face Flies (Musca autumnalis)
Pasture
Named after where it likes to congregate, this known vector of cattle eye diseases is often found on the faces of cattle. They feed on secretions around the eyes, nose and mouth of cattle and can carry infection-causing bacteria, including bovine pink eye, to the animal. This pest develops in fresh, undisturbed manure.
You’ll know this by:
- - Similar to house fly in size
- - Yellowish/orange stripes abdomen on males
- - Sponging mouthpart

Horn Flies (Haematobia irritans)
Pasture
Typically found clustered on the backs of cattle, the horn fly feeds on the blood larger livestock, taking up to 40 blood meals a day. Horn flies rarely leave their hosts, with the females leaving only to lay their eggs in fresh manure. With the stress caused by loss of blood and energy dislodging the pests, cattle affected by horn flies often have reduced weight gains, lower feed efficiency and decreased milk yields.
You’ll know this by:
- - Smaller in size compared to other flies
- - Brownish grey to black coloring
- - Piercing, sucking mouthparts

Stable Flies (Stomoxys calcitrans)
Confined
Stable flies are biting insects that primarily target the legs of livestock. The females painful bites can cause stress and discomfort, leading to decreased weight gain and overall productivity in cattle and other animals.
You’ll know this by:
- - Distinct checker-board pattern on the abdomen
- - Similar size to house and face flies
- - Dull-gray color

House Flies (Musca domestica)
Confined
The house fly may not directly feed on livestock but can always be found in close association to humans and livestock feeding on various organic matter such as feed stuffs, animal manure and garbage. This pest can thrive in manty environments and can quickly build in numbers, with the females laying up to 150 eggs at time.
You’ll know this by:
- - Four distinct stripes on the thorax
- - Sponging mouthparts
- - Pale yellowish abdomen
FLIES FACTS
-
GENERAL FLY BEHAVIOR
- Active during the day
- Seek out livestock and feed on blood
- Cause irritation and stress to animals
-
GENERAL FLY INFESTATION SITES
- Animal Barns and Shelters
- Feedlots
- Pasture Areas
- Manure Piles
- Composting Areas
- Waste Disposal Areas
- Watering Holes
- Rotting Vegetation
- Outdoor Feeding Stations
- Manure Handling Equipment
-
GENERAL SIGNS OF FLY INFESTATIONS
- Excessive Fly Presence
- Agitated Livestock
- Wounds or Sores on Livestock
- Restlessness and Discomfort in Animals
- Flies on Livestock
-
THE DANGERS OF FLIES
- Spread of Diseases
- Irritation and Stress
- Reduced Feed Efficiency
- Contamination of Food and Water
- Economic Losses
- Impact on Human Health
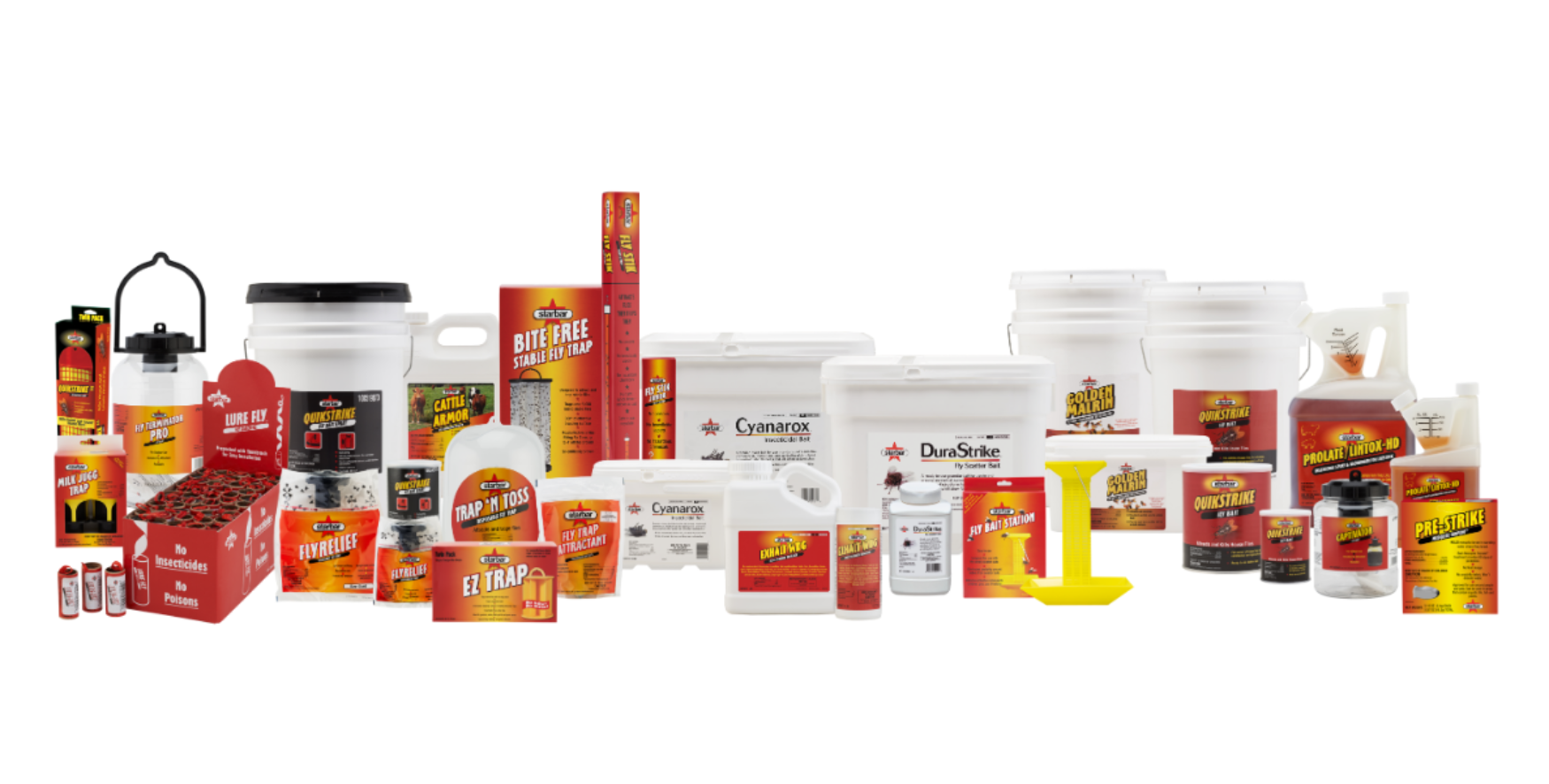
PROFESSIONAL FLY CONTROL PRODUCTS
Baits
Starbar® fly baits and abatement strips are for use at low levels of your operation. Featuring a range of active ingredients, Starbar® fly baits can be used together as part of a rotational program to combat fly resistance.
Sprays
Starbar® sprays are used in, on and around your operation. With a wide variety of solutions, these products help to fight a wide variety of insects.
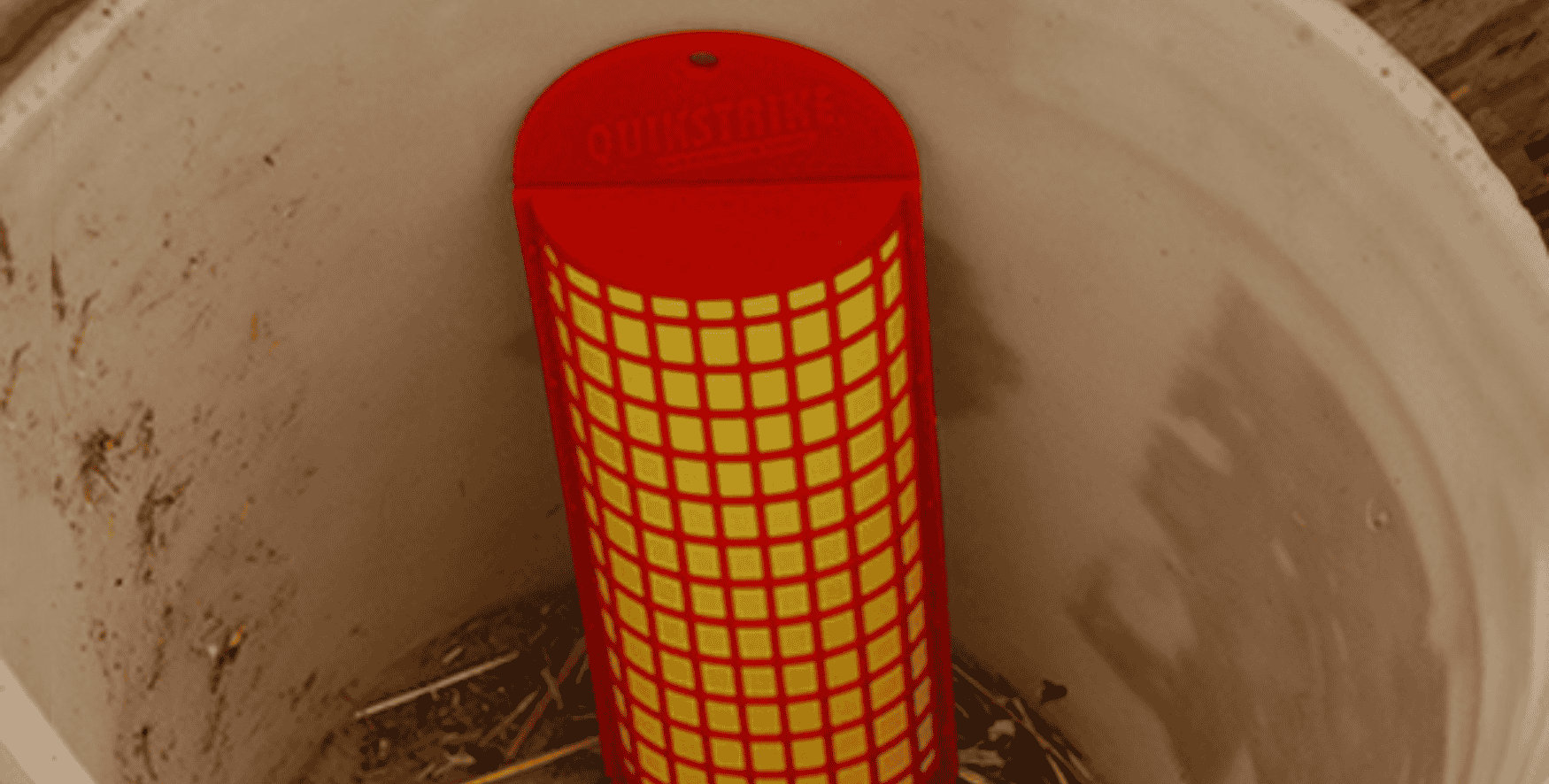
Traps
Each trap is designed to address the specific behavior of the fly at each level. That’s targeted fly control based on science.